MDK: Model Development Kit
MDK: Model Development Kit
MDK, IPSEpro’s Model Development Kit, offers all the capabilities needed to define new equipment models and translate them into a form that can be used by PSE (IPSEpro's Process Simulation Environment). MDK consists of two main functional units: the Model Editor, and the Model Compiler.
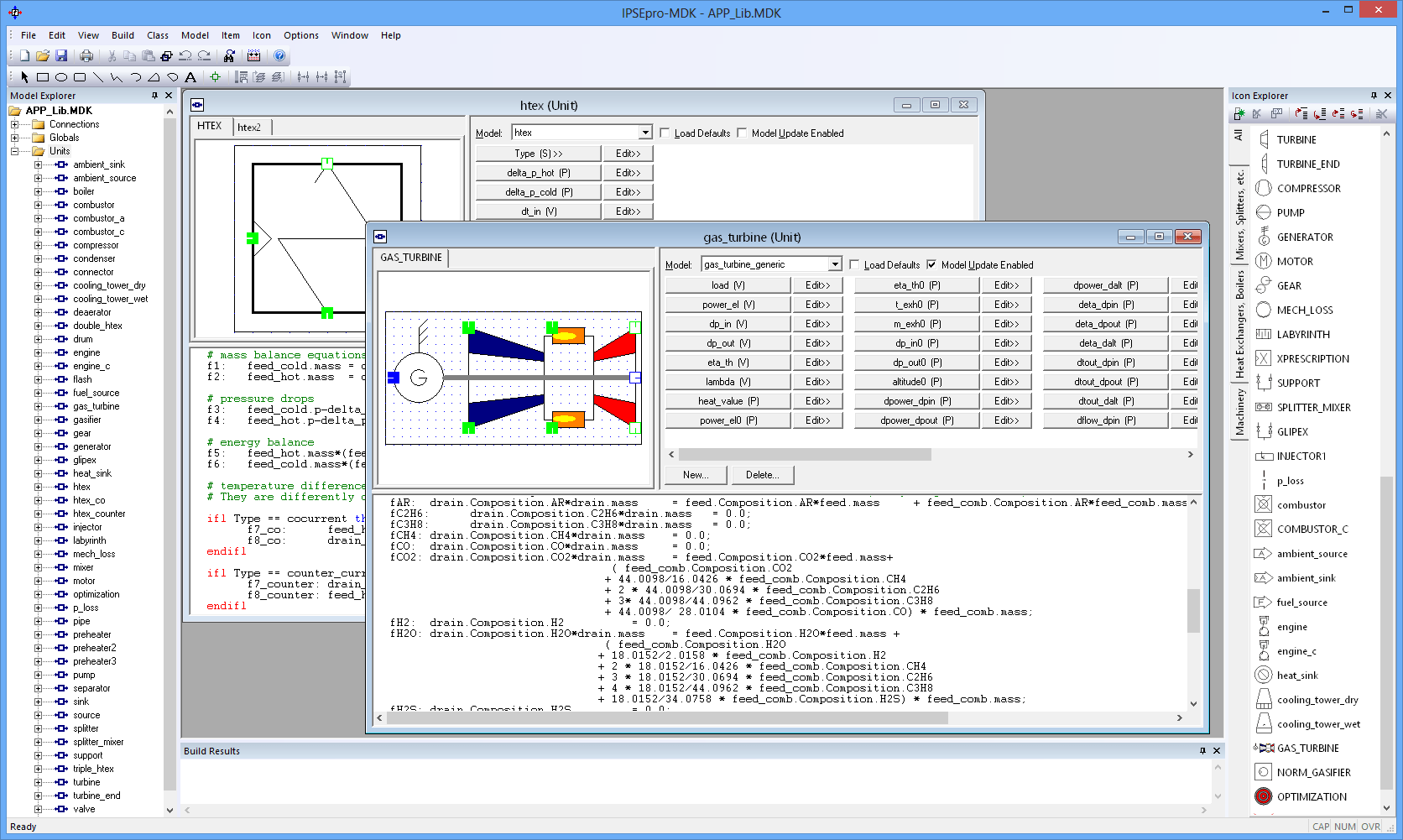
The model editor allows the user to design icons that represent equipment models and to describe the model behavior mathematically.
The model editor allows the user to design icons that represent the models and to describe the model behavior mathematically.
MDK, IPSEpro’s Model Development Kit, offers all the capabilities needed to define new equipment models and translate them into a form that can be used by PSE (IPSEpro's Process Simulation Environment). MDK consists of two main functional units: the Model Editor, and the Model Compiler.
The model editor allows the user to design icons that represent equipment models and to describe the model behavior mathematically.
Model Description Language
MDK provides a model description language (MDL) to describe models mathematically. MDL is intuitive since it is based on standard mathematical notations. It is closely integrated with the user interface.
Simple MDL Code Sample
f1: feed.mass = drain.mass;
f2: time_s/3600 = time_h;
f3: if abs(dt_in/dt_out) >=1.2 || abs(dt_out/dt_in) >=1.2 then
q_trans*ln(dt_in/dt_out)/(dt_in-dt_out) = htc_area
else q_trans*2.0/(dt_in+dt_out) = htc_area;
t1: test (mass >=0.0) warning "mass flow negative";
Notice several important facts:
- In MDL the user actually writes an equation, not assignments as in traditional programming languages. Therefore, in MDL it is permitted to use expressions on the left hand side.
- The sequence in which the equations are written is irrelevant for the actual solution process. PSE’s solver determines the optimum solution sequence independently, according to the process model you've built. So you can write the MDL equations in any order you wish.
- MDL allows you to use conditional statements ("if" statements) inside an equation.
- In the example above “t1” is a test condition. If this condition is not satisfied at the end of a solution process, PSE issues a warning.
- Equation-oriented modeling: the equations defined in the MDK will be solved using the equation-oriented solvers integrated into the IPSEpro PSE module.
Model Compiler
MDK’s model compiler translates the model descriptions into a binary format that guarantees high performance when a process model is solved in PSE.

Model Description Language
MDK provides a model description language (MDL) to describe models mathematically. MDL is intuitive since it is based on standard mathematical notations. It is closely integrated with the user interface.
Simple MDL Code Sample
f1: feed.mass = drain.mass;
f2: time_s/3600 = time_h;
f3: if abs(dt_in/dt_out) >=1.2 || abs(dt_out/dt_in) >=1.2 then
q_trans*ln(dt_in/dt_out)/(dt_in-dt_out) = htc_area
else q_trans*2.0/(dt_in+dt_out) = htc_area;
t1: test (mass >=0.0) warning "mass flow negative";
Notice several important facts:
- In MDL the user actually writes an equation, not assignments
as in traditional programming languages. Therefore, in MDL it is permitted to use expressions on the left hand side.
- The sequence in which the equations are written is irrelevant for the actual solution process. PSE’s solver determines the optimum solution sequence independently, according to the process model you've built. So you can write the MDL equations in any order you wish.
- MDL allows you to use conditional statements ("if" statements) inside an equation.
- In the example above “t1” is a test condition. If this condition is not satisfied at the end of a solution process, PSE issues a warning.
- Equation-oriented modeling: the equations defined in the MDK will be solved using the equation-oriented solvers integrated into the IPSEpro PSE module.
Model Compiler
MDK’s model compiler translates the model descriptions into a binary format that guarantees high performance when a process model is solved in PSE.
RECEIVE MORE INFORMATION ABOUT ENGINOMIX PRODUCTS AND SERVICES:
Enter your information below to access sample models and to receive more information about Enginomix Products and Services.
Thank you for contacting us.
We will get back to you as soon as possible
We will get back to you as soon as possible
Oops, there was an error sending your message.
Please try again later
Please try again later

